Anterior Cruciate Ligament - ACL Surgery Cost in India
About Anterior Cruciate Ligament - ACL Surgery
What Is ACL Surgery and Why Is It Done?
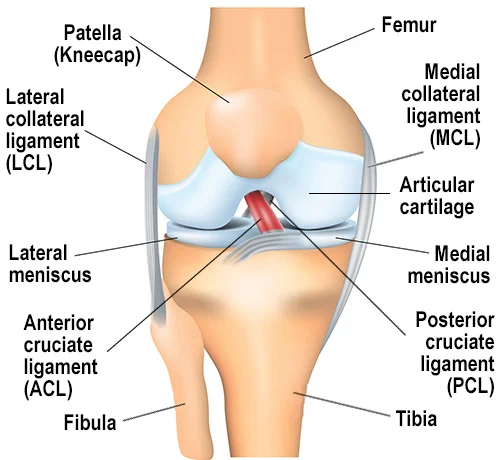
The anterior cruciate ligament (ACL) is one of the major ligaments in the knee joint. It connects the thigh bone (femur) to the shinbone (tibia). The anterior cruciate ligament helps stabilize the knee during activities that involve pivoting, sudden stops, or changes in direction, such as sports, climbing stairs, or even walking on uneven surfaces.
An ACL tear often occurs due to sports injuries, road accidents, or sudden twisting movements. When the ACL is wholly or partially torn, it can lead to knee instability, swelling, pain, and restricted movement. In many cases, especially among athletes or active individuals, this damage cannot heal on its own and requires surgical intervention.
ACL surgery (commonly known as ACL reconstruction or ACL repair surgery) is performed to restore knee stability. It does so by replacing the torn ligament with a graft. This graft can be taken from the patient's own tissue (autograft) or from a donor (allograft). The procedure is done using arthroscopic (keyhole) surgery, which ensures quicker recovery and minimal scarring.
Timely ACL reconstruction not only improves joint function but also prevents long-term damage to the knee cartilage and meniscus, reducing the risk of developing early arthritis.
When Do Doctors Recommend ACL Surgery?
Doctors recommend ACL surgery when the ligament damage in the knee significantly affects stability, mobility, or daily function and when non-surgical treatments are unlikely to restore full knee function. The decision is based on the extent of the tear, the patient's lifestyle, age, and future activity goals.
One of the most common triggers for recommending ACL reconstruction is complete ligament rupture, where the torn ACL cannot regenerate or heal naturally. In such cases, the knee often becomes unstable, making it difficult to walk, run, or change direction without the joint buckling or "giving way."
ACL surgery is also advised when:
- The patient has chronic instability, which persists even after rest and physiotherapy.
- There is a concurrent injury to other structures in the knee, like the meniscus or collateral ligaments.
- The patient is a young athlete or an active adult who intends to return to high-impact sports or physically demanding jobs.
- Repeated knee injuries occur because of the weak ligament, increasing the risk of cartilage damage.
- Rehabilitation alone fails to restore full strength, motion, or confidence in the joint.
Doctors use clinical tests (like the Lachman test) and MRI imaging to assess ligament damage. Suppose the torn ACL is not providing the necessary mechanical stability (especially for those with active lifestyles). In that case, surgical reconstruction becomes the preferred route to prevent long-term damage and help the patient regain optimal knee performance.
What are the Different Types of ACL Surgery Procedures?
ACL surgery is not a one-size-fits-all procedure. Orthopedic surgeons choose the most suitable technique based on the patient's age, activity level, type of injury, and personal preferences. The primary goal is to reconstruct the torn ligament using a graft that replaces the damaged ACL, restoring strength and stability to the knee.
The main types of ACL reconstruction procedures are:
- Autograft ACL Reconstruction: In this technique, the graft is harvested from the patient's own body. It is the most commonly used approach, especially for athletes and active individuals.
- Patellar Tendon Autograft: Surgeons take the middle third of the patellar tendon, along with small pieces of bone from the kneecap and shinbone. This method provides strong fixation and is ideal for high-performance individuals, but may cause anterior knee pain post-surgery.
- Hamstring Tendon Autograft: A portion of the hamstring tendons (usually semitendinosus and sometimes gracilis) is taken from the same leg. This technique has less risk of anterior knee pain and a quicker healing time at the donor site.
- Quadriceps Tendon Autograft: Less commonly used, this involves harvesting part of the quadriceps tendon with or without bone. It's often chosen when other graft options are not suitable, especially in revision surgeries.
- Allograft ACL Reconstruction: Here, the graft is taken from a donor (cadaver) rather than the patient. Allografts reduce surgery time and eliminate donor site pain but carry a slightly higher risk of graft failure in young athletes due to slower integration. This method is usually reserved for older adults or revision surgeries.
- Synthetic Grafts (Rarely Used): Artificial grafts made of synthetic materials were experimented with in the past, but due to a high failure rate and complications, their use is now infrequent and discouraged in most countries.
- Revision ACL Surgery: In cases where a previous ACL reconstruction has failed due to reinjury or graft weakening, a revision surgery is performed. It is more complex and may require different graft sources or bone grafting techniques.
Each of these procedures has its benefits and limitations. The choice of graft type and method depends on the surgeon's expertise, the patient's anatomy, and long-term activity goals.
How is ACL Surgery Done?
ACL reconstruction surgery typically follows a minimally invasive approach using arthroscopy. It allows surgeons to visualize and repair the joint through small incisions, ensuring faster recovery and minimal scarring.
- Preoperative Preparation: The surgical team begins by evaluating the patient through a detailed clinical examination, MRI scans, and blood tests. On the day of surgery, the medical team administers general or spinal anesthesia. The surgical site is cleaned and sterilized to prevent infection.
- Arthroscopic Examination of the Knee: The surgeon creates two or three small incisions near the knee joint. A tiny camera with light (arthroscope) is inserted into the joint, transmitting real-time images onto a monitor. It allows the surgeon to clearly see the torn ACL and assess any associated damage to the cartilage or meniscus.
- Graft Harvesting: If using an autograft, the surgeon removes a tendon (hamstring, patellar, or quadriceps) from the patient's own body. If an allograft is planned, the sterilized donor tissue is prepared in advance. The graft is then cleaned, shaped, and sized to fit the knee.
- Tunnel Creation in Bones: Using precision surgical tools, the surgeon drills small tunnels in the femur (thigh bone) and tibia (shin bone). These tunnels form a pathway for the new graft to be placed in the exact position of the original ACL.
- Graft Placement and Fixation: The surgeon threads the graft through the tunnels and positions it to mimic the natural alignment of the ACL. They then secure the graft with screws, buttons, or staples to anchor it firmly to the bone. It stabilizes the knee and allows the graft to integrate over time.
- Closure and Dressing: Once the graft is fixed, the surgeon irrigates the joint with sterile solution to remove any debris or loose particles. Ortho surgeons close the incisions with sutures or surgical tape. A sterile bandage is applied, and the leg is placed in a brace or immobilizer to support early healing.
- Postoperative Monitoring: Hospital staff moves the patient to a recovery area for observation. Doctors monitor vital signs and manage pain with medications. Most patients go home the same day or after a short overnight stay, depending on their condition.
After surgery, a structured physiotherapy program begins almost immediately to help the knee regain strength, motion, and function. Full recovery often takes 6 to 9 months, but many patients start walking with assistance within a few days.
Get a Free Treatment Plan
About Anterior Cruciate Ligament - ACL Surgery in India
What is the Cost of ACL Surgery in India?
The cost of ACL surgery in India ranges between ₹1,50,000 and ₹3,00,000, which is approximately $1,800 to $3,600. This price makes India one of the most cost-effective countries in the world for high-quality ligament reconstruction, especially when compared to Western nations where the same procedure can cost over $15,000.
This all-inclusive price usually covers:
- Surgeon consultation and surgical fees
- Pre-surgical diagnostic tests such as X-ray, MRI, and blood work
- Operation theatre and anesthesia charges
- Graft material cost (autograft or allograft)
- 1–2 days of hospital stay
- Medications and consumables
- Post-surgery physiotherapy sessions (initial phase)
- Follow-up consultations
It is important to note that the final cost may vary slightly depending on the hospital, city, and the type of graft used. For instance, a patellar tendon autograft may cost less than an allograft, which is sourced from a donor and processed under sterile conditions.
Leading orthopedic centers in India, including Fortis, Apollo, and Medanta, provide ACL surgery with world-class infrastructure, US/UK-trained surgeons, and international patient support.
Breakdown of ACL Surgery Cost in India
To help patients better understand what they are paying for, here's a detailed breakdown of ACL surgery costs in India. The total cost typically falls between ₹1,50,000 and ₹3,00,000 (or $1,800 to $3,600), depending on the hospital, city, and surgical approach used.
- Surgeon's fee and operation theatre charges usually cost between ₹60,000 to ₹90,000, depending on the surgeon's experience and hospital reputation.
- Graft material, whether autograft or allograft, adds ₹20,000 to ₹40,000 to the bill. Allografts may be slightly more expensive due to donor tissue processing.
- Anesthesia and intraoperative medications generally cost around ₹15,000 to ₹25,000, covering both general/spinal anesthesia and drugs used during surgery.
- A hospital stay of 1 to 2 days, including room charges and nursing care, may cost ₹25,000 to ₹40,000, depending on the type of room (shared/private).
- Diagnostic imaging like MRI and X-rays usually cost ₹10,000 to ₹20,000 before surgery.
- Initial physiotherapy sessions post-surgery, especially during hospital stay and early recovery, add about ₹5,000 to ₹10,000.
Cost Component | Estimated Cost (INR) | Estimated Cost (USD) |
| Surgeon’s Fees and OT Charges | ₹60,000 – ₹90,000 | $720 – $1,080 |
| Graft Material (Autograft/Allograft) | ₹20,000 – ₹40,000 | $240 – $480 |
| Anesthesia and Medications | ₹15,000 – ₹25,000 | $180 – $300 |
| Hospital Stay (1–2 Days) | ₹25,000 – ₹40,000 | $300 – $480 |
| Diagnostic Tests (MRI, X-rays) | ₹10,000 – ₹20,000 | $120 – $240 |
| Physiotherapy (Initial Phase) | ₹5,000 – ₹10,000 | $60 – $120 |
| Total Estimated Cost | ₹1,50,000 – ₹3,00,000 | $1,800 – $3,600 |
ACL Surgery Cost Comparison With Other Countries
ACL surgery in India is significantly more affordable compared to many Western and Asian countries, without compromising on surgical quality, hospital infrastructure, or recovery outcomes.
Country | Average Cost (USD) | Remarks |
| India | $1,800 – $3,600 | Includes surgery, hospital stay, grafts, diagnostics, and follow-ups |
| United States | $15,000 – $25,000 | High due to hospital charges, surgeon fees, and lack of package pricing |
| United Kingdom | $10,000 – $18,000 | NHS covers limited cases; private surgery is expensive |
| Canada | $12,000 – $20,000 | Free for citizens via public healthcare; long wait times, and not for expats |
| Singapore | $9,000 – $16,000 | High-quality care but costly for international patients |
| UAE / Dubai | $8,000 – $14,000 | Advanced care, but expensive due to high facility fees |
| Thailand | $4,000 – $6,500 | Affordable but slightly costlier than India |
| Turkey | $4,000 – $7,000 | Popular in Europe and the Middle East for orthopedic care |
Why India Is More Cost-Effective
- Indian hospitals offer all-inclusive packages that cover everything from pre-surgery evaluations to rehab guidance.
- Internationally trained surgeons and advanced arthroscopic technology match Western standards.
- Medical tourism-friendly policies and affordable infrastructure keep operational costs low.
- High patient volume ensures faster surgery slots, even for complex ACL tears or revision surgeries.
So while ACL surgery in the US or UK may exceed $15,000 without insurance, India offers the same procedure at less than one-fourth the cost, with shorter wait times and comprehensive care.
What are the Factors Affecting ACL Surgery Cost in India?
The cost of ACL reconstruction surgery can vary widely, even within the same country. Several factors influence the final price a patient pays.
- Type of Graft Used: Allografts are usually more expensive due to processing, sterilization, and storage requirements. In contrast, autografts are cost-effective but may involve more surgical time and post-op recovery.
- Surgeon's Experience and Expertise: Highly experienced orthopedic surgeons, especially those with international training or sports medicine backgrounds, may charge higher fees.
- Hospital Category and Facilities: The cost of ACL surgery differs between multi-specialty corporate hospitals (like Fortis, Medanta, Apollo) and smaller local clinics.
- City of Treatment: Cities like Delhi NCR, Mumbai, Bangalore, and Chennai tend to have slightly higher prices compared to tier-2 cities like Jaipur, Indore, or Kochi.
- Hospital Stay Duration: While ACL surgery is often a 1-day procedure, some patients may require extended stays due to complications or co-existing conditions. Additional nights in private or deluxe rooms will increase the overall bill.
- Pre-Surgery Tests and Imaging: If the patient hasn't had recent imaging (like an MRI), it must be done before surgery. The cost of tests like X-rays, MRIs, and blood panels can vary based on the lab and location.
- Postoperative Physiotherapy: While some hospitals include a few initial sessions in the package, long-term rehab (especially sports-focused) adds to the total expense if taken outside the hospital.
What Services are Available for International Patients Seeking ACL Surgery in India?
India has become a top destination for medical tourists seeking ACL surgery, thanks to its combination of affordability, high-quality care, and specialized support for overseas patients. Top orthopedic hospitals in India provide various services to international patients. Some of them are:
Pre-Arrival Support
- Online Consultation and Medical Evaluation: Patients can share medical reports and receive a treatment plan and cost estimate in advance.
- Visa Invitation Letter and Assistance: Hospitals provide medical visa invitation letters to help patients and accompanying family members get their visas without delay.
- Travel Planning and Appointment Scheduling: Dedicated coordinators help with flight planning, priority surgery booking, and doctor availability.
Arrival and Hospital Coordination
- Airport Pickup and Drop Services: Chauffeured transport is arranged for international patients upon arrival and discharge.
- Language Interpreters: Multilingual staff and interpreters are available to help patients communicate comfortably with doctors and nurses.
- Dedicated International Patient Lounge: Major hospitals have exclusive international wings or patient lounges to offer a hassle-free experience with concierge support.
During the Treatment
- Personal Case Manager: Each patient is assigned a coordinator who manages scheduling, medical paperwork, financial arrangements, and daily support.
- Customized Accommodation Options: Hospitals or partner agencies assist with budget hotels, guest houses, or serviced apartments near the treatment facility.
- Attendant Facilities: Facilities for one or more family members to stay, along with meal arrangements and local transport.
Post-Surgery Support
- Physiotherapy and Rehab Planning: On-site and home-based rehab options are arranged to aid knee recovery before the patient travels back.
- Discharge Summary and Travel Clearance: Patients receive detailed records, imaging, medication lists, and fitness-to-fly certificates before departure.
- Teleconsultation and Follow-up Care: Virtual follow-up appointments are arranged post-discharge to monitor progress and provide ongoing guidance.
These services are often bundled into a single treatment package that simplifies the cost and care process for medical tourists. Whether you're traveling from the Middle East, Africa, Europe, or Southeast Asia, India's international patient programs ensure safe, efficient, and comfortable care.
Recovery and Success Rate of ACL Surgery
ACL reconstruction is a highly successful procedure when performed by skilled surgeons using modern arthroscopic techniques. However, recovery is a gradual process and varies from person to person depending on age, physical condition, and commitment to physiotherapy.
Recovery Timeline After ACL Surgery
- First 1–2 Weeks: Patients begin walking with the help of crutches. Swelling and pain reduce with rest, cold therapy, and medications. Early physiotherapy starts to restore joint motion and prevent stiffness.
- Week 3 to Week 6: Patients regain control over leg muscles. Supervised physical therapy focuses on regaining full extension and flexion of the knee. Most patients stop using crutches by the end of this phase.
- Weeks 7 to 12: Strength training is introduced. Balance and stability exercises improve muscle coordination. Patients can walk, climb stairs, and do low-impact activities comfortably.
- Months 4 to 6: Patients resume light jogging and functional movements like squatting or jumping. By the 5th or 6th month, athletes can start sport-specific training under supervision.
- 6 to 9 Months: Full return to sports like football, basketball, and skiing is typically allowed only after a complete assessment of strength, agility, and knee stability.
Success Rate of ACL Surgery in India
India reports a success rate of over 90–95% for ACL reconstruction in top-tier hospitals. Success is defined by:
- Complete restoration of knee stability and range of motion
- Absence of repeated knee buckling or instability
- Patient's ability to return to regular or athletic activity
- Minimal postoperative complications
Hospitals in India follow international rehabilitation protocols and use modern graft fixation methods (interference screws, EndoButtons, etc.) that ensure secure and long-lasting outcomes. Some of the factors that support better recovery are:
- Early physiotherapy guided by trained professionals
- Patient adherence to rehab exercises and follow-up visits
- Use of high-quality graft materials and fixation devices
- Experienced surgical teams performing the procedure
With expert care, most patients can walk without support within a few weeks and return to sports in 6 to 9 months.
Anterior Cruciate Ligament - ACL Surgery Cost Comparison by Country
Compare Anterior Cruciate Ligament - ACL Surgery costs across different countries to make an informed decision about your medical treatment.
| Country | Cost Range (USD) | Potential Savings | Action |
|---|---|---|---|
INIndiaCurrentBest Value | $1,800 - $3,600 | — | Get Quote |
Note: Costs may vary based on hospital choice, room type, additional services, and individual medical requirements. Contact us for a personalized quote.
FAQ
Browse by Department
Explore procedures in different departments
Get a Free Treatment Plan
Our website uses cookies. By clicking on accept you give your consent to the use of cookies as per our Privacy Policy.
